🧪 O-Level Periodic Table Mastery: What You Must Know for Your Chemistry Paper
Hey there future A1 scorers! 😎 Are you ready to master the Periodic Table and crush your Chemistry paper? Whether you love Chemistry or just trying to survive it, this guide will make sure you know exactly what’s tested, how to study smart, and avoid common mistakes! 💥💯
🔍 Why the Periodic Table Is So Important at O-Levels
Let’s be real — the Periodic Table is the heart of Chemistry. ❤️ You’ll use it in almost every paper — Paper 1 (MCQ), Paper 2 (Structured), and sometimes even in planning questions for Paper 3 (SPA-alike)!
So… why does it matter so much? 🤔
Because it helps you:
-
Understand element properties
-
Predict chemical reactions
-
Memorise trends and groups
-
Ace bonding, atomic structure, and more!
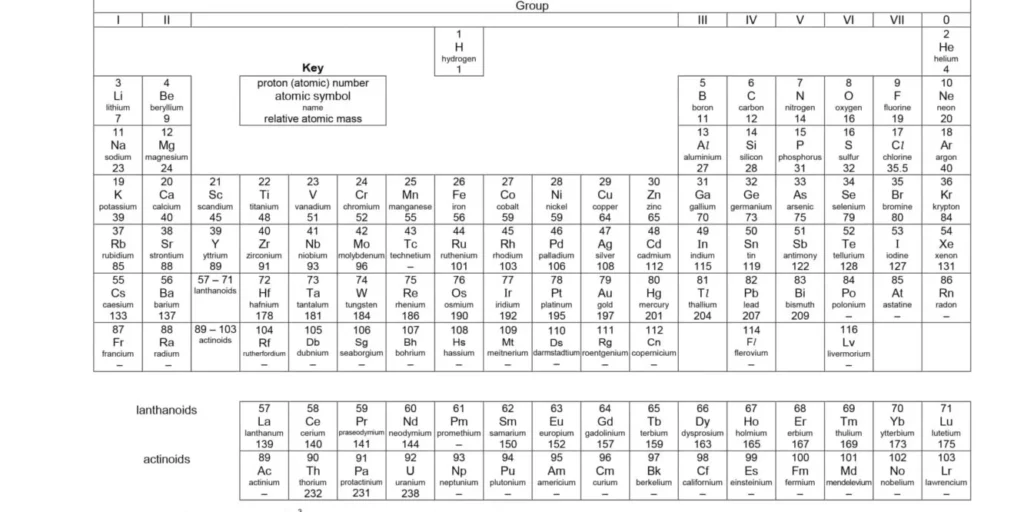
📃 What the Periodic Table Looks Like in O-Level Exams
✅ Good news! You don’t have to memorise the whole thing.
📌 You get a simplified Periodic Table in the exam.
But here’s the catch:
You must know how to USE it, not just stare at it like a mystery box. 😅
It includes:
-
Symbols 🧲 (e.g. H for Hydrogen)
-
Atomic numbers 🔢
-
Mass numbers (sometimes)
-
Group and Period info
🧱 Periodic Table Basics: Let’s Break It Down!
1. 🧪 Elements: What Are They?
-
A substance made of only one type of atom
-
Cannot be broken down further by chemical means
-
Each element has its own spot in the Periodic Table
2. 🧠 Atomic Number = Number of Protons
This number tells you:
-
Which element it is (e.g. 1 = Hydrogen)
-
The number of electrons in a neutral atom
🗒️ Example: Atomic number 11 = 11 protons = 11 electrons → Sodium!
3. 💡 Mass Number = Protons + Neutrons
Used to:
-
Calculate neutron number
-
Understand isotopes
🧮 Neutrons = Mass number – Atomic number
🧭 Periods vs Groups: Know the Layout!
📚 Periods = Rows (Left to Right)
-
Tells you the number of electron shells
-
E.g. Period 2 = 2 shells
🏢 Groups = Columns (Top to Bottom)
-
Tells you the number of valence electrons
-
Determines chemical properties!
🔥 Must-Know Groups for O-Level Chem
1. Group I – Alkali Metals ⚠️
-
Examples: Li, Na, K
-
1 valence electron
-
Soft, low density
-
Very reactive, especially with water 💦
-
Form alkaline solutions (hence “alkali”)
🧪 Reaction with water:
💡 Trend:
-
Reactivity increases down the group
2. Group VII – Halogens 🌈
-
Examples: F, Cl, Br, I
-
7 valence electrons
-
Non-metals, coloured gases/liquids/solids
-
Form salts with metals (e.g. NaCl)
-
Displacement reactions are tested a lot!
📊 Trend:
-
Reactivity decreases down the group
-
Colour gets darker and melting/boiling point increases
🧪 Example: Cl₂ displaces Br⁻ from solution
3. Group 0 – Noble Gases 😇
-
Examples: He, Ne, Ar
-
Full outer shell → very unreactive
-
Monatomic gases
-
Used in light bulbs, balloons, neon lights
🧠 Remember: Stability = Full outer shell
🔬 Transition Metals: The Fancy Guys 💼
-
Found in the middle block (Groups 3–12)
-
High melting points, high densities
-
Good conductors of electricity 🔌
-
Can have multiple oxidation states (Fe²⁺ and Fe³⁺!)
-
Form coloured compounds (💙 Cu²⁺ = blue!)
🧪 They are often used as catalysts in industry (e.g. Iron in Haber Process)
📈 Trends Across the Periodic Table (Must-Know!)
As You Go Across a Period (Left → Right):
-
Atomic size decreases 📉
-
Nuclear charge increases ➕
-
Metallic → Non-metallic
-
Valence electrons increase
As You Go Down a Group:
-
Atomic size increases 📈
-
Electron shells increase
-
Reactivity:
-
Group I = More reactive
-
Group VII = Less reactive
-
🧠 Common Confusions to Avoid!
🚫 Confusing Group vs Period
Group = vertical, same number of valence electrons
Period = horizontal, same number of shells
🚫 Memorising instead of understanding trends
Don’t just cram. Understand why reactivity changes.
🚫 Forgetting displacement reactions
Displacement is a HOT topic — always tested!
🚫 Assuming noble gases are boring
You’ll lose marks if you forget why they’re stable!
💯 How to Study the Periodic Table Effectively
✅ Tip 1: Use Colour-Coded Charts 🎨
Group I = 💛
Group VII = 💚
Group 0 = 💜
Transition Metals = 🔵
Make your notes visual and fun!
✅ Tip 2: Flashcards (Element Name → Properties)
-
What group? Period?
-
Metal or non-metal?
-
Physical properties?
-
Reaction examples?
🧠 Active recall is 🔑
✅ Tip 3: Practice Displacement Questions
Cl₂, Br₂, I₂ with different halide salts.
Write equations, observe colour changes 🧪
✅ Tip 4: Mnemonics Make Life Easy 😄
🎶 Group I: “Little Naughty Kids Rub Cake in Fire”
(Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr)
🎶 Group VII: “Funny Clowns Break Ice At Times”
(F, Cl, Br, I, At, Ts)
🎶 Transition: Just remember your Iron, Copper, Zinc, Chromium pals!
📝 Exam Question Types You’ll Face
🔍 Paper 1 (MCQ):
-
Identify elements
-
Predict reactions
-
Periodic trends
✍️ Paper 2 (Structured):
-
Describe reactivity down a group
-
Explain trends using atomic structure
-
Balanced equations
🧪 Paper 3 (Practical / Planning):
-
Predict outcomes based on element position
📦 Sample Questions You MUST Practice
Q1: Why is sodium more reactive than lithium?
🧠 Answer: Sodium has more electron shells, so its outer electron is further from the nucleus. Less nuclear attraction → easier to lose → more reactive.
Q2: Why is chlorine able to displace bromine from potassium bromide?
🧠 Answer: Chlorine is more reactive than bromine because it is higher up in Group VII. More reactive halogens can displace less reactive ones.
Q3: What are 2 properties of transition metals?
🧠 Answer:
-
Form coloured compounds
-
Have high melting points
-
Can have variable oxidation states
🧠 Quick Recap Summary!
| Concept | Must Know Facts |
|---|---|
| Group I | 1 valence electron, very reactive metals |
| Group VII | 7 valence electrons, coloured, reactive |
| Group 0 | Full shell, unreactive, gases |
| Periods | Horizontal rows → no. of electron shells |
| Groups | Vertical columns → same no. of valence e⁻ |
| Transition metals | Coloured, catalysts, multiple valencies |
| Trends (Across) | Smaller atoms, more non-metallic |
| Trends (Down) | Larger atoms, different reactivity patterns |
🎯 Final Exam Strategy – How to Ace It
✅ Understand, don’t memorise blindly
✅ Learn by groups and trends, not individual facts
✅ Practice MCQs and structured questions
✅ Review common experiments with elements
✅ Use past papers with your periodic table side-by-side
🔥 Quickfire Revision Quiz (Test Yourself!)
-
Which group has full outer electron shells?
-
What happens to atomic size across a period?
-
Which is more reactive: K or Na?
-
What is the colour of copper(II) sulfate solution?
-
Can bromine displace chlorine?
(Answers below!)
✅ Answers:
-
Group 0 (Noble gases)
-
Decreases
-
K (Potassium)
-
Blue
-
No (Bromine is less reactive)
📚 Extra Resources
-
📱 Chemistry flashcard apps like Quizlet
-
🎥 YouTube channels: FuseSchool, CrashCourse Chemistry
💬 Final Words from Your Chemistry Senior 💙
Don’t wait till the last minute to understand the Periodic Table. It’s not just for nerds or top students — it’s your secret weapon to score smart in Chemistry. 🧠💥
Whether you’re aiming for a B3 or an A1, mastering the Periodic Table will get you there. You got this! 🚀
🎓 Need help with Chemistry?
Join our top-tier O-Level Chemistry Tuition with customised lessons, top school tutors, and fun + exam-smart teaching!
👉 Book a FREE trial now at Sophia Education!
📞 Or WhatsApp us: +65 8875 0044